 The information on this site is from one of the most famous books about the New Medicine (GNM / 5BN): "The Psychic Roots of Diseases" by Björn Eybl. Since September 2025, it is available in the form of an app with many additional features.
The information on this site is from one of the most famous books about the New Medicine (GNM / 5BN): "The Psychic Roots of Diseases" by Björn Eybl. Since September 2025, it is available in the form of an app with many additional features.It was written in german and was translated into more than 10 languages already. German is not freely available, as the rights are held by a publisher, but all these translations are available as ebooks / PDFs for free, as a gift of Björn for you, for the New Earth, for a new time.
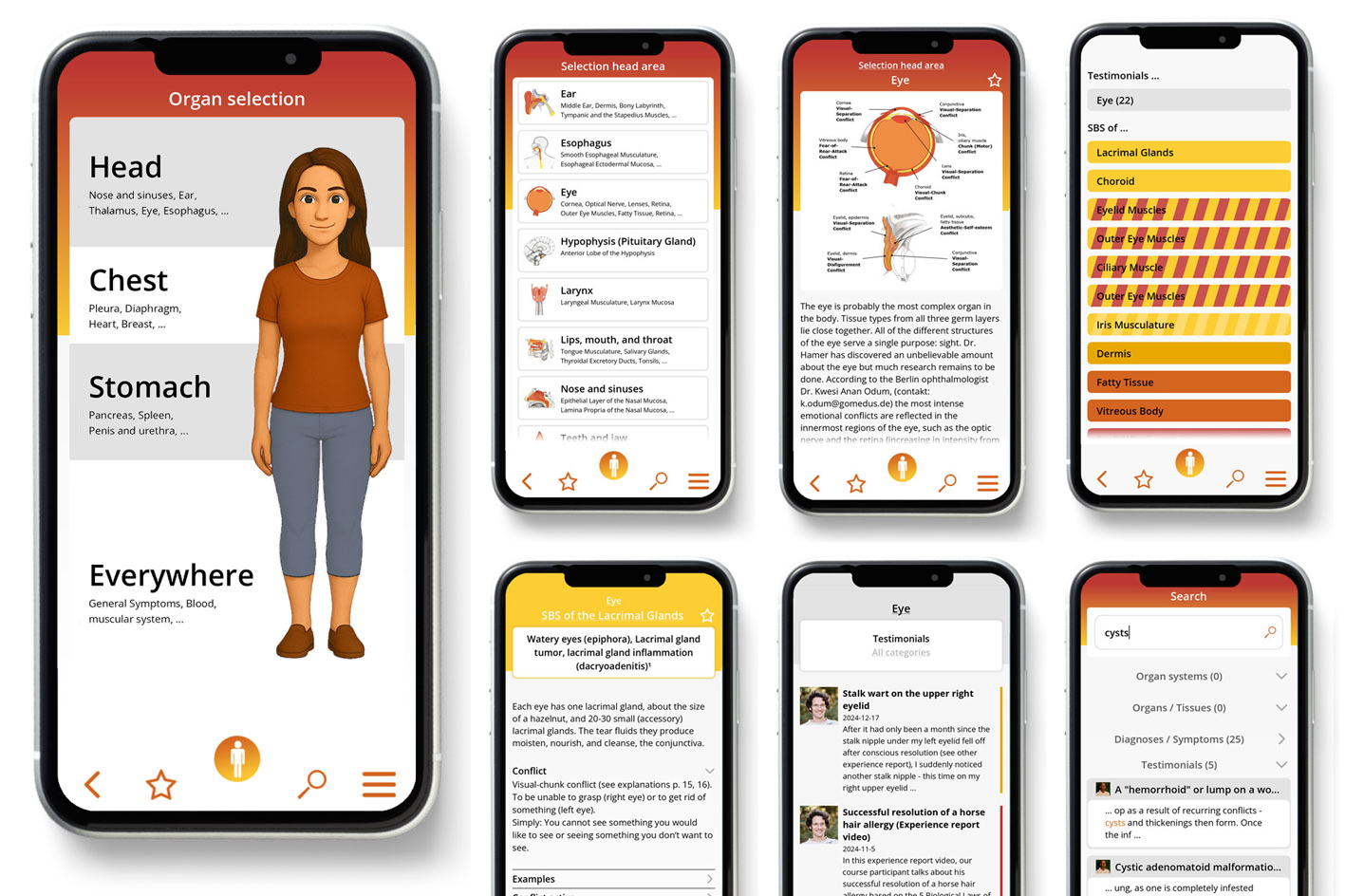
In cooperation with Björn, it is splitted on "Disease is Different" into the sections by organ systems and combined with the real cases of our international testimonial / report archive of the related organ system.
PLEURA
The pleura lines the chest cavity. It is controlled by the cerebellum and is made up entirely of mesodermal tissue. The pleura has two layers: the outer layer (pleura parietalis) is attached to the chest cavity, while the inner layer (pleura pulmonalis) forms the outer layer of the lungs. The very thin space (pleural cavity) between the two layers is filled with a fluid that allows the lungs to glide during breathing.
Pleura
Attack-to-the-chest
or chest cavity


Cancer of the pleura (pleura mesothelioma, pleura cancer)1
| Conflict | Attack-to-the-chest conflict. Real attack/threat or imagined threat. Fear concerning the lungs, heart, ribs and thoracic spine. |
|---|---|
| Examples | ➜ Severe pain in the chest cavity (lungs, chest, heart, ribs, thoracic spine). • A person is diagnosed with a roundish shadow on the lung (lung cancer) = attack-to-the-chest conflict. During the conflict-active phase he develops a pleura mesothelioma. (Archive B. Eybl)  Fifteen years ago, a thin woman gets breast cancer (adeno-ca). Having become acquainted with the 5 Biological Laws of Nature she lets the tumor be and lives very well with it. Unfortunately, 6 years ago, she allows a biopsy to be taken. Afterwards the breast does not heal shut and for three years she lives with an open wound. At this point she becomes frightened and suffers an attack-to-the-chest conflict > growth of a pleura mesothelioma. After the breast is surgically closed (skin closure), the patient comes into healing with a pleural effusion. (Archive B. Eybl) Fifteen years ago, a thin woman gets breast cancer (adeno-ca). Having become acquainted with the 5 Biological Laws of Nature she lets the tumor be and lives very well with it. Unfortunately, 6 years ago, she allows a biopsy to be taken. Afterwards the breast does not heal shut and for three years she lives with an open wound. At this point she becomes frightened and suffers an attack-to-the-chest conflict > growth of a pleura mesothelioma. After the breast is surgically closed (skin closure), the patient comes into healing with a pleural effusion. (Archive B. Eybl) |
| Conflict-active | Cell proliferation in the pleura. Growth of a pleura mesothelioma. Either flat or patchy growth, depending on the kind of attack perceived. Possibly a recurring conflict. |
| Bio. function | Protection of the chest cavity by thickening of the pleura. |
| Repair phase | Tubercular, caseating degradation of tissue: inflammation of the pleura (pleuritis), pain, fever, night sweats, breathing difficulties, chest pain, pleural effusion due to syndrome. |
| Repair crisis | Chills, severe pain. |
| Note | Most cancers diagnosed in the pleura can be attributed to diagnosis shocks and are interpreted by CM as “metastases.“ – The prognosis is correspondingly poor. With knowledge of the 5 Biological Laws of Nature, there will be fewer cases of pleural tumors in the future and fewer people will die of them. |
| Questions | Symptoms since when? (Determine the phase, because complaints normally begin after the onset of the repair phase). Which type of attack did I experience? (OP, diagnosis, physical fight, accident, etc.). Can I handle diagnoses in general? Which conditioning is this based on? (Childhood, ancestors)? |
| Therapy | Determine the conflict and conditioning and, if possible, resolve them in real life. The most important therapy is the knowledge of the biological interrelations. Guiding principles: “I am surrounded by a wall of crystal.“ “I am safe and protected.“ “Nobody and nothing can do any harm to me.“ Lymph drainages (see p. 68), acupoint massage (see p. 68, breathing exercises. CM treats with surgery, chemotherapy and radiation and is content with extending their life expectancy prognosis by three months. Right after the surgery, mesothelioma usually grow back into the OP wound. Our view (and the view“from the view of the pleura“) is that this is logical, because the surgery represents another attack. > Not recommended due to low chances of success. |
Pleurisy, accumulation of pus in the pleura (pleural empyema), pleural adhesions (fibrinous or granulomatous pleurisy)2
| Phase | Repair phase: degradation of the pleural tumors. Inflammation, severe pain while breathing, especially with dry pleuritis – fever, night sweats. Growths due to chronically recurring-conflicts (triggers). |
|---|---|
| Therapy | The conflict is resolved. Support the healing. The greatest problem is the pain. Cannabis works gently and relieves pain. Damp chest or whole-body wraps with brine, enzyme preparations, lymph drainages (see p. 68), colloidal silver internally. CM pain medication if necessary. |
Pleurisy or adhesions caused by dust (e.g., asbestos pleurisy)
| Phase | Repair phase or persistent conflict: degradation of a pleural tumor. Although the pleura has no direct contact with dust, it can co-react to the conflict: The inhalation of dust is unpleasant for everyone. Constant or intensive inhalation can lead to a dust-attack conflict to the lung. “This dust is toxic and I have to breathe it in all the time!“ > growth of a pleura mesothelioma > inflammation of the pleura in the repair phase with pain, Fever, night sweats. Pleural callosities (plaque) due to this usually being a recurring–conflict. |
|---|---|
| Therapy | For recurrences: Determine the conflict and conditioning and, if possible, resolve them in real life. It is likely that it will be necessary to avoid any source of dust. Massages, lymph drainage massages (see p. 68), enzyme preparations, breathing exercises for cleaning and strengthening. CM pain medication. |
Collection of fluid in the pleura that comes from the pleura itself (exsudative pleural effusion)2
Here the protein content is about 30 g/l. SBS same as above (see: p.209), but in addition – syndrome (see: p.277).
| Example |  A patient is found to have cysts of the branchial arches. CM‘s diagnosis: “non-Hodgkin‘s lymphoma.“ He is told that they must do major surgery on his chest cavity in order to get to both sides = attack-to-the-chest conflict. After the surgery, the patient dies of massive pleural effusions on both sides. (See Dr. Hamer, Goldenes Buch Vol. 2, p. 135) A patient is found to have cysts of the branchial arches. CM‘s diagnosis: “non-Hodgkin‘s lymphoma.“ He is told that they must do major surgery on his chest cavity in order to get to both sides = attack-to-the-chest conflict. After the surgery, the patient dies of massive pleural effusions on both sides. (See Dr. Hamer, Goldenes Buch Vol. 2, p. 135) |
|---|---|
| Phase | Repair phase or persistent conflict– fluid is collected between the inner and outer layers of the pleura, due to the degradation of the tumor = “sweating out“ of the pleura. To a certain extent, this is normal because fluid forms during every inflammation. In combination with syndrome, however, the effusion can become threatening. Exudative pleural effusions are rich in protein. This is where the problem with punctures lies. Due to repeated draining of fluid, the body loses large volumes of protein > lowered albumin level. Low blood protein content leads to a drop in the colloid osmotic pressure in the blood system which promotes fluid collection = 1st vicious circle. At the psychic level, a puncture can set off another vicious circle that is even worse if the painful and risky puncture procedure (pneumothorax danger) is perceived as an attack-to-the-chest conflict = 2nd vicious cycle. Nevertheless, punctures are sometimes unavoidable. Usually a recurring–conflict. |
| Therapy | The attack conflict is resolved. Support the healing. Address the kidney collecting tubules conflict (see 277), if present. Lymph drainages (see p. 68). Salt water baths or wraps. MMS (see p. 68). Cannabis (CBD) oil, enzyme preparation. Tea: stinging nettle, horsetail, goldenrod. Intake of biologically valuable protein (e.g., eggs, quark). Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) 3% internally, vitamin D3, cod liver oil (see p. 68). Puncture (tap) only as a last resort. Possible albumin infusions. No infusions with salt. Gradual lengthening of the intervals between punctures. |
Collections of fluid in the pleura that comes from the surroundings (transudative pleural effusion)
Through transudative pleural effusion (protein content of less than 30 g/l), fluid seeps from inflamed surrounding tissues into the pleural cavity. This can be the case with a weak heart (cardiac insufficiency p. 154), low blood protein levels (hunger edema), or with healing ribs, breastbone, thoracic vertebrae, lungs or bronchi. There is significant accumulation of water only during syndrome.
| Conflict | Not an SBS of the pleura, but another SBS (usually bone) combined with syndrome. |
|---|---|
| Example |  A woman with breast cancer undergoes radiation and chemotherapy. This makes the breast small and unsightly, which results in a local self-esteem conflict with respect to the breastbone. As she enters the repair phase, the healing bone presses the resulting fluid into the pleura = transudative pleural effusion. (See Dr. Hamer, Goldenes Buch vol. 2, p. 364) A woman with breast cancer undergoes radiation and chemotherapy. This makes the breast small and unsightly, which results in a local self-esteem conflict with respect to the breastbone. As she enters the repair phase, the healing bone presses the resulting fluid into the pleura = transudative pleural effusion. (See Dr. Hamer, Goldenes Buch vol. 2, p. 364) |
| Therapy | See exudative pleural effusion and causative SBS above. |
All experience reports on the organ system „Pleura“ from the International Report Archive:
| Author | Title and Overview | Keywords |
|---|
